Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disease characterized by the increase in blood sugar.
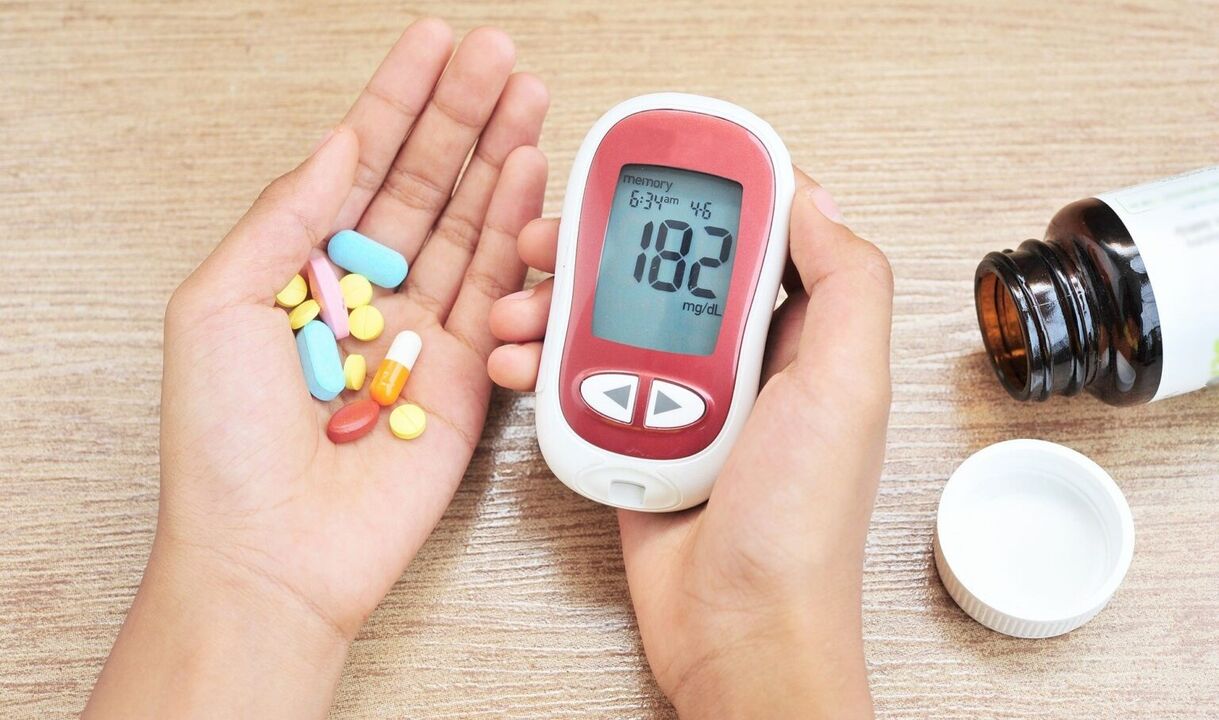
The disease occurs as a result of a defect in insulin production defects, insulin or both of these factors. In addition to increasing blood sugar, the disease manifests itself in urine, release of sugar, thirst, fat, protein and mineral metabolism and developing complications.
- Type 1 diabetes (autoimmune, idiopathic): Destruction of beta cells of the pancreas producing insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - a defect, which dominates insulin production without insulin or insulin production or sensitivity with tissues.
- Gestational sugar in diabetes occurs during pregnancy.
- Other species:
- genetic defects;
- diabetes caused by drugs and other chemicals;
- diabetes caused by infections;
- Removal of pancreas, trauma, pancreas, acromegali, izino - Kushinka, thyrootoxicosis and others.
- Easy Current: There are no complication.
- The degree of moderate violence: damage to the eyes, kidneys and nerves.
- Violent current: distant complications of diabetes.
The main symptoms of the disease have such manifestations:
- Plenty of urine and increased thirst;
- Increased appetite;
- General weakness;
- Leaves skin lesions (eg vitiligo), vagina and urinary tract, are often observed in non-essential patients in the disadvantage;
- The voice of the vision causes changes in the slippery media of the eye.
Type 1 diabetes usually starts at a young age.
Type 2 diabetes are usually diagnosed in people aged 35-40.
The diagnosis of the disease is based on blood and urine tests.
In order to diagnose the glucose concentration in the blood is determined (an important situation was re-proclaimed in growing sugar and other days).
After the test, a blank stomach or 2 hours later:
- Venous blood - 3. 3-5. 5 MMOL / L;
- Capillary blood - 3. 3-5. 5 MMOL / L;
- Blood venous plasma - 4-6. 1 mmol / l.
In an empty stomach:
- 6. 1 mmol / l;
- capillary blood 6. 1 mmol / l;
- Venous Blood Plasma 7. 0 more than 0 mmol / l.
Whether at any time of the day, regardless of food time:
- Venous blood is 10 MMOL / L;
- capillary blood 11, 1 mmol / l;
- Venous blood plasma is more than 11, 1 mmol / l.
The level of Glycali blood hemoglobin in diabetes exceeded 6, 7-7, 5%.
The content of the C-Peptide allows you to assess the functional state of beta cells. In patients with type 1 diabetes, this level generally increased sharply in patients in type 2 diabetics, patients with insulinum in normal or growing patients.
Immuniosisactive insulin concentration increased by 1, normal or type 2.
Glucose diagnosis of glucose diagnosis for diabetes, bloody disease, injury or surgical intervention, glucose hormones, thyroid hormones, thyroid hormones, thyroid hormones, thiahids, beta-blockers, etc. the liver.
In the urine in diabetes, the glucose appears only after exceeding the "kidney threshold" (about 180 mg 9. 9 mmol / l). It is characteristic of important fluctuations and growth with age; Therefore, the definition of glucose in urine is considered sensitive and unreliable test. The test serves as a general reference point for a significant increase in blood sugar (glucose) and is used for daily observation of the dynamics of the disease.
In a significant part of diabetes, 5-10% of the blood sugar indicators are improving the significant and significant reduction in dietary advice. One of the main conditions is the regularity of physical power (for example, 30 minutes of walking daily, swim 1 hour 3 times a week). Glucose concentration in blood>13-15 mmol / l, physical activity is not recommended.
In addition to light and medium physical strength, additional use of carbohydrates without more than 1 hour, additional use of carbohydrates is required before and after the load (15 grambes to digest 15 g in each 40 minutes). Medium physical effort, which is more than 1 hour and intensive sport, should reduce 20-50% of the insulin dose operating 6-12 hours after physical activity.
Dietary treatment (Table № 9), carbohydrate exchange is aimed at normalizing and preventing fat metabolism.
Insulin preparations for the treatment of diabetes are divided into 4 categories:
- Ultra -core movement (the start of the action - the period of action after 15 minutes is 3-4 hours).
- Quick movement (the start of the action - in 30 minutes. - 1 hour; 6-8 hours of action.
- The average term of the activity (start of the action is 1-2, 5 hours, the period of the movement is 14-20 hours).
- Long action (after 4 hours of movement; the period of action is up to 28 hours).
Destination Mode Insulin mode is seriously selected for each patient with an individual or dialitologist or endocrinologist.
When built on the subtle injection site, the needle needs to create a skin layer to prevent the skin under the skin and not entering the muscle tissue. The skin of the skin should be widely covered, the thickness of the skin layer is less than the length of the needle should enter an angle of 45 °.
When choosing a place for injection, you need to avoid compressed skin areas. Injection locations cannot be changed without system. There are no injections on shoulder skin.
- Short-term insulin preparations should be carried out to subcutaneous oil fiber of the abdominal front wall 20-30 minutes ago.
- LONG -FCECT insulin preparations are presented to the Bud or Omba subcutaneous oil fiber.
- Ultra -Short insulin injections are carried out immediately before eating and immediately after eating.
Heat and physical activity increases insulin absorption rate and reduces the cold.